
使用 Python 解释器交互模式
在终端(tty)输入并执行指令时,我们说解释器是运行在 交互模式(interactive mode)。在这种模式中,它会显示 主提示符(primary prompt),提示输入下一条指令,通常用三个大于号(>>>)表示;连续输入行的时候,它会显示 次要提示符,默认是三个点(...)。进入解释器时,它会先显示欢迎信息、版本信息、版权声明,然后就会出现提示符:
$ python3
Python 3.9 (default, June 4 2019, 09:25:04)
[GCC 4.8.2] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>多行指令需要在连续的多行中输入。比如,以 if 为例:
>>> the_world_is_flat = True >>> if the_world_is_flat: ... print("Be careful not to fall off!") ... Be careful not to fall off!
Python 交互模式查看整个命令历史
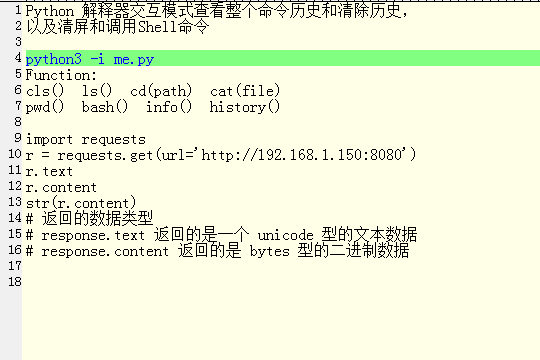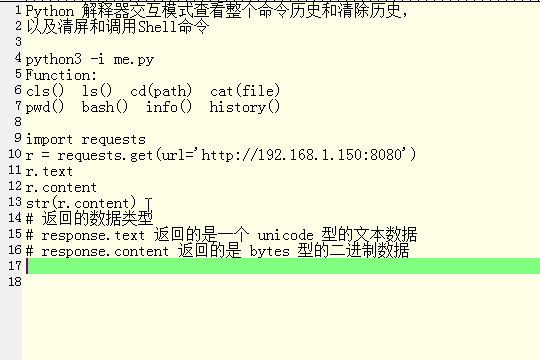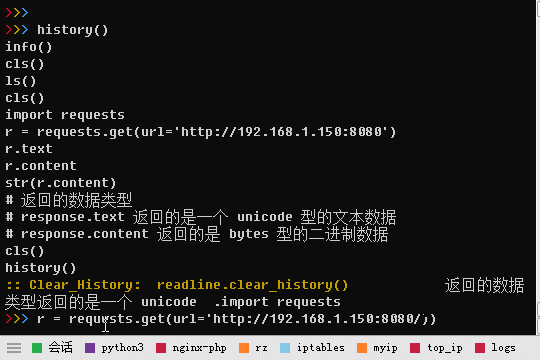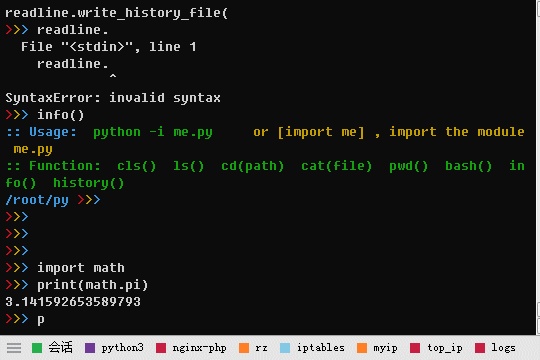
如何在交互式python中看到整个命令历史?
import readline def history(): for i in range(readline.get_current_history_length()): print(readline.get_history_item(i + 1)) print(':: Clear_History: readline.clear_history() ')- readline.get_current_history_length() 获取预设的历史命令条数。
- readline.get_history_item(id) 获取id指定的历史命令。
- readline.clear_history() 清除历史命令记录
- readline.read_history_file('test.py') 把test.py文件读取到历史命令
Python 自动补全模块 readline 解析
- readline模块定义了一系列函数用来读写Python解释器中历史命令,并提供自动补全命令功能。这个模块可以通过relcompleter模块直接调用,模块中的设置会影响解释器中的交互提示,以及内置函数raw_input()和input()提供的提示。
readline模块定义了以下方法: 输入
readline.然后按TAB就能自动补全显示>>> readline. readline.add_history( readline.read_history_file( readline.append_history_file( readline.read_init_file( readline.clear_history( readline.redisplay( readline.get_begidx( readline.remove_history_item( readline.get_completer( readline.replace_history_item( readline.get_completer_delims( readline.set_auto_history( readline.get_completion_type( readline.set_completer( readline.get_current_history_length( readline.set_completer_delims( readline.get_endidx( readline.set_completion_display_matches_hook( readline.get_history_item( readline.set_history_length( readline.get_history_length( readline.set_pre_input_hook( readline.get_line_buffer( readline.set_startup_hook( readline.insert_text( readline.write_history_file( readline.parse_and_bind(使用 Python 交互模式学习,使用
history()函数可以方便提取整理命令语句
import requests r = requests.get(url='http://192.168.1.150:8080') r.text r.content str(r.content) # 返回的数据类型 # response.text 返回的是一个 unicode 型的文本数据 # response.content 返回的是 bytes 型的二进制数据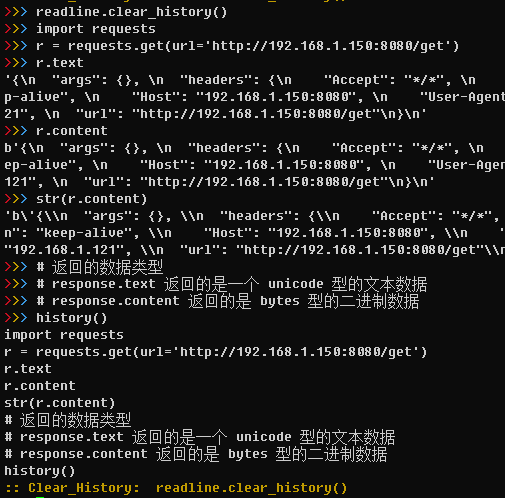
Python 交互模式 历史命令、清屏和调用Shell模块 git.io/me.py
:: Usage: python -i me.py or [import me] , import the module me.py
:: Function: cls() ls() cd(path) cat(file) pwd() bash() info() history()源码:me.py
#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import sys, os, readline # define Color Green = '\033[32m'; Red = '\033[31m' GreenBG = '\033[42;37m'; RedBG = '\033[41;37m' Yellow = '\033[0;33m'; SkyBlue = '\033[0;36m'; Font = '\033[0m' sys.ps1 = Red + '>' + Yellow + '>' + SkyBlue + '> ' + Font sys.ps2 = SkyBlue + '... ' + Font def cls(): # print('\x1bc') os.system('clear') def pwd(): print( SkyBlue + os.getcwd(), end = ' ') def ls(): cur_path = os.getcwd() os.system('ls -l ' + cur_path) pwd() def cd(path = '.'): os.chdir(path) pwd() def cat(file = 'me.py'): with open(file, 'r') as f: print(f.read()) def bash(): os.system('bash') def history(): for i in range(readline.get_current_history_length()): print(readline.get_history_item(i + 1)) print( Yellow + ':: Clear_History: readline.clear_history() ') def info(): print( SkyBlue + ':: Usage: ' + Green + 'python -i me.py' + Yellow + ' or [import me] , import the module me.py') print( Green + ':: Function: cls() ls() cd(path) cat(file) pwd() bash() info() history()') pwd() info(); c = cls; h = historypython 变量可以指向函数
以Python内置的求绝对值的函数abs()为例,调用该函数用以下代码:
>>> f = abs >>> f <built-in function abs> >>> f(-8) 8- 所以执行
c = cls; h = history语句,就可以 c 和 h 简写调用函数了
python windows 安装 readline 模块
python -m pip install pyreadline
# 不能直接用pip install pyreadline